If you are wondering what health approach wins the showdown between cardio vs strength training, this is the post for you.
You’ve committed to early runs, five days a week, yet the scale barely moves. You’ve probably heard the debates: “Cardio burns more calories!” vs. “Strength training builds muscle that burns fat!” The truth? Both claims hold weight, but neither tells the full story.
In fact, cardio can burn up to 600-800 calories per hour, depending on intensity, while strength training elevates your resting metabolic rate and increases post-workout burn through EPOC (excess post-exercise oxygen consumption). Still, weight loss isn’t just about calorie math – it’s about body composition, hormone balance, and long-term sustainability.
We’ll break down how each training style supports weight loss differently, so you can make the right call for your goals, your lifestyl,e and how you want to feel in your own body.
What is Cardio?
Cardio is any aerobic exercise that raises your heart rate and keeps it elevated for at least 10 minutes. It includes activities like walking, jogging, cycling and swimming. These movements use large muscle groups repeatedly and rhythmically.
Cardiovascular training strengthens your heart and lungs. It improves how efficiently your body moves oxygen through the bloodstream. Cardio improves endurance, supports fat loss, and increases energy. Whether done indoors or outdoors, consistent cardio training helps your body use energy more effectively throughout the day.
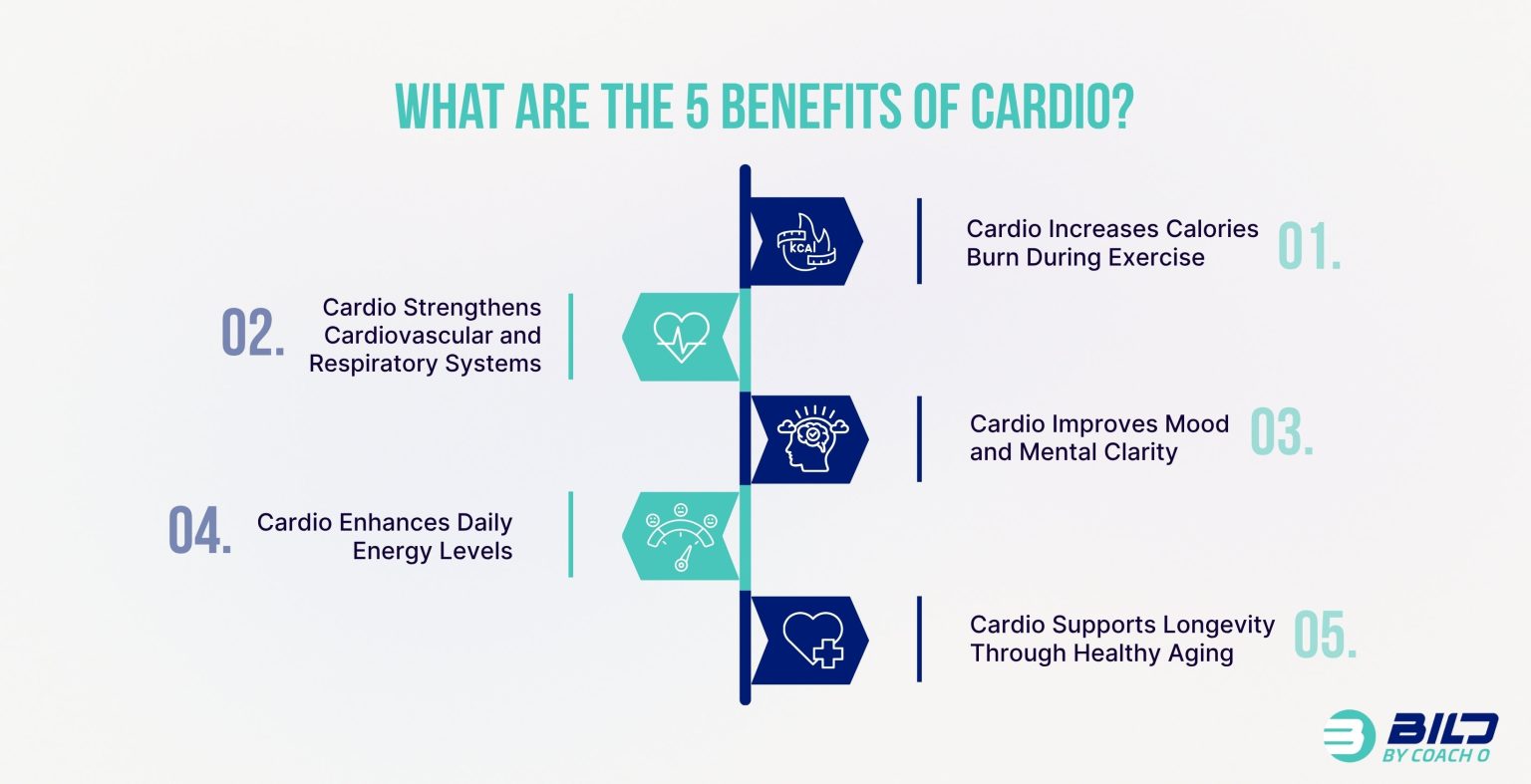
What are the 5 Benefits of Cardio?
Cardio supports weight loss, heart health, and mental clarity. Below are the five main benefits of cardio exercise for fat loss and overall health:
1. Cardio Increases Calories Burn During Exercise
Cardio burns between 400 and 800 calories per hour, depending on the intensity; higher-intensity workouts, such as HIIT, increase total energy output in less time. A steady jog burns 500-600 calories per hour. A brisk walk burns 200-300.
2. Cardio Improves Heart and Lung Function
Cardio strengthens your heart and lungs. It improves circulation, lowers resting heart rate, and helps regulate blood pressure. Regular cardio exercise supports long-term heart health and reduces the risk of hypertension.
3. Cardio Improves Mood and Mental Clarity
Cardio triggers the release of endorphins and serotonin. These hormones reduce stress, improve mood, and help regulate sleep. One 20-minute cardio session can reduce anxiety and improve clarity.
4. Cardio Enhances Daily Energy Levels
Cardio improves blood circulation and cellular oxygen use. These changes boost energy by up to 40% in regular walkers. Short sessions reduce fatigue and improve focus throughout the day.
5. Cardio Supports Longevity Through Healthy Aging
Cardio lowers the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. It supports joint mobility and preserves independence. Moderate-intensity cardio helps adults over 50 stay active and mobile.
Top 3 Effective Cardio Exercises for Weight Loss
The most effective cardio exercises for fat loss combine calorie burn, low impact and time efficiency. These three workouts support consistent fat reduction without needing a gym or complex gear.
- Brisk Walking or Elliptical – Best for Beginners
Brisk walking and elliptical workouts burn 200-300 calories in 30 minutes. These low-impact options reduce joint stress and support fat loss. Walk outdoors, on a treadmill or during breaks. Ellipticals offer similar benefits with added upper-body movement.
- Jogging or Jump Rope – Best for Short, Intense Sessions
Jogging and jump rope raise your heart rate quickly and improve cardiovascular capacity. Jogging burns 400–500 calories per 30 minutes. Jumping rope burns 10–15 calories per minute and improves coordination. These exercises are ideal for time-crunched schedules.
- HIIT or Sprint Intervals – Best for Maximum Calorie Burn
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) and sprints burn up to 800 calories per hour. These sessions alternate short bursts of full effort with brief recovery periods. HIIT boosts metabolism for up to 24 hours. Sprint intervals can be done on a track, hill or treadmill.

What is Strength Training?
Strength training is exercise that uses resistance to increase muscle mass and physical strength. Resistance can come from dumbbells, barbells, kettlebells, resistance bands, machines or body weight.
When muscles work against resistance, they grow stronger and more efficient. This process, called progressive overload, improves muscle tone, increases metabolism and supports joint health. Strength training reshapes your body by reducing fat and building lean tissue.
Unlike cardio, strength workouts continue to burn calories after the session ends. The increased metabolic activity from muscle repair raises your resting calorie burn through a process known as EPOC (excess post-exercise oxygen consumption).

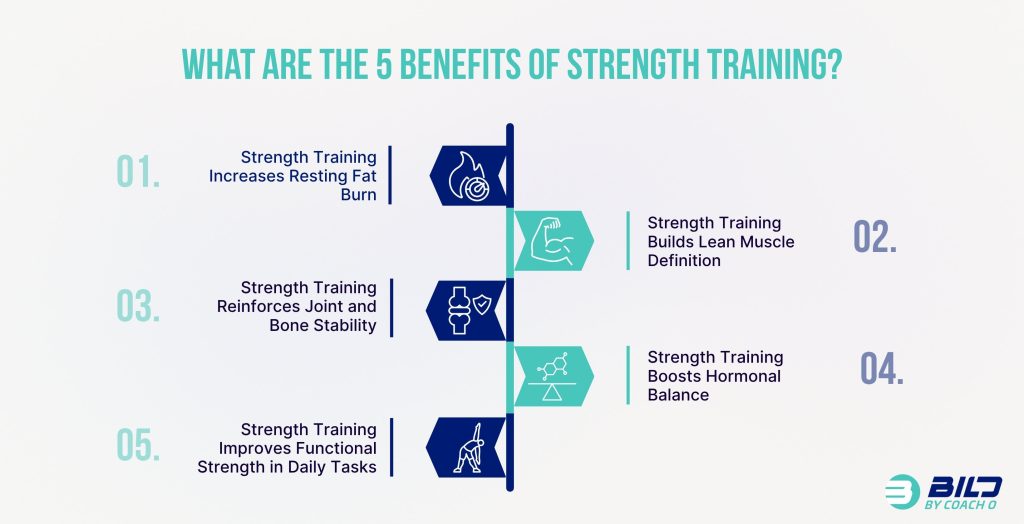
What are the 5 Benefits of Strength Training?
Strength training supports fat loss, builds lean muscle and improves functional performance. These five benefits of strength training explain why resistance workouts are essential for long-term health and body composition.
1. Strength Training Increases Resting Fat Burn
Strength training increases your resting metabolic rate (RMR). Muscle burns more calories than fat, even at rest. The repair process after lifting creates an extended calorie burn known as EPOC (excess post-exercise oxygen consumption).
2. Strength Training Builds Lean Muscle Definition
Strength workouts stimulate muscle growth and improve body composition. Muscle gives your body a more defined and athletic appearance. This process improves strength without creating excess bulk.
3. Strength Training Reinforces Joint and Bone Stability
Lifting weights reinforces muscles around joints and increases bone density. These improvements reduce the risk of injury and improve balance, especially in adults over 40. Strong joints support long-term mobility.
4. Strength Training Boosts Hormonal Balance
Strength workouts stimulate growth hormone and testosterone, which support muscle repair and fat metabolism. In women, strength training also improves insulin sensitivity and supports estrogen balance.
5. Strength Training Improves Functional Strength in Daily Tasks
Lifting improves your ability to move, lift and carry in everyday life. These improvements reduce fatigue and help with tasks like lifting groceries, climbing stairs or playing with your kids.
Top 3 Effective Strength Training Exercises for Weight Loss
The most effective strength exercises for fat loss target large muscle groups and raise your heart rate. These three movements build strength, burn calories, and require minimal equipment.
- Bodyweight Squats – Best for Lower Body Activation
Squats target your glutes, quads, and hamstrings – the body’s largest muscle groups. They increase lower-body strength, elevate heart rate and improve core engagement. Start with 2– 3 sets of 10– 15 reps using a controlled form. - Dumbbell Rows – Best for Posture and Upper-Body Strength
Rows build strength in the upper back, arms, and core. They improve posture and sculpt lean muscle along the spine and shoulders. Use light to moderate dumbbells and perform 2 sets of 12– 15 reps on each side. - Resistance Band Presses – Best for Joint-Safe Upper Body Training
Resistance band presses activate your chest, shoulders and triceps. Bands apply constant tension while protecting the joints. Perform 2–3 sets of 12 reps with slow, controlled movement.

Cardio vs Strength Training: Pros and Cons for Weight Loss
Cardio and strength training support weight loss through different mechanisms. Cardio burns more energy during the workout. Strength training builds muscle and increases fat burn after exercise ends.
| Metric | Cardio | Strength Training |
| Calories Burned | High during workouts: 400–800 kcal per hour | Moderate during session; higher post-exercise burn via EPOC |
| Body Composition | Reduces total fat mass | Reduces fat and increases lean muscle mass |
| Long-Term Fat Loss | Requires frequent, high-volume sessions | Improves resting metabolism and sustains fat loss long-term |
| Muscle Preservation | May reduce muscle if no resistance is used | Builds and preserves muscle while reducing body fat |
| Time Efficiency | Short bursts (HIIT) are effective; steady-state sessions require more time | Efficient with compound lifts and circuits |
| Metabolic Boost | Short-term increase during and shortly after activity | Long-term increase through muscle development and recovery |
Cardio or Strength Training: Which Helps You Lose More Weight?
Cardio burns more calories during a single session. Strength training increases long-term fat loss by raising resting metabolism. Each method affects weight loss differently, and the best results come from aligning your workouts with your goals.
Do You Lose More Weight with Cardio or Strength Training?
Yes, cardio results in faster scale weight loss. Strength training promotes long-term fat reduction. Running or cycling for 30-60 minutes burns 400-800 calories. Strength workouts burn fewer calories during the session but raise your resting metabolic rate (RMR) through muscle growth and repair.
Cardio often shows quicker results on the scale. Strength training builds lean tissue, which burns fat at rest. Over time, this leads to healthier body composition and sustained fat loss.

What’s More Effective to Reduce Belly Fat: Cardio or Weights?
Any form of exercise directly targets belly fat. Both cardio and strength training reduce overall body fat. Belly fat includes visceral fat, which decreases through improved insulin sensitivity, hormone regulation, and calorie deficit.
Strength training helps preserve muscle while reducing total fat. Cardio increases total energy expenditure. A combined approach reduces belly fat more effectively than either method alone.
How to Combine Cardio and Strength Training for Better Results?
Combining strength and cardio leads to greater fat loss, better muscle retention and improved overall fitness. Each method contributes differently: strength training boosts metabolism, while cardio increases energy expenditure during workouts.
Weekly Workout Routines Combining Strength and Cardio for Weight Loss
Integrating both strength training and cardiovascular exercise into your weekly routine is one of the most effective ways to lose weight sustainably. A balanced workout schedule helps you preserve lean muscle mass while burning calories, improving cardiovascular health and boosting metabolism.
How Often to Train
- Strength Training: 2-3 sessions per week
- Cardio: 2-3 sessions per week
- Total Workouts: 5-6 days per week
- Rest Days: 1-2 per week to support recovery, especially in a calorie deficit
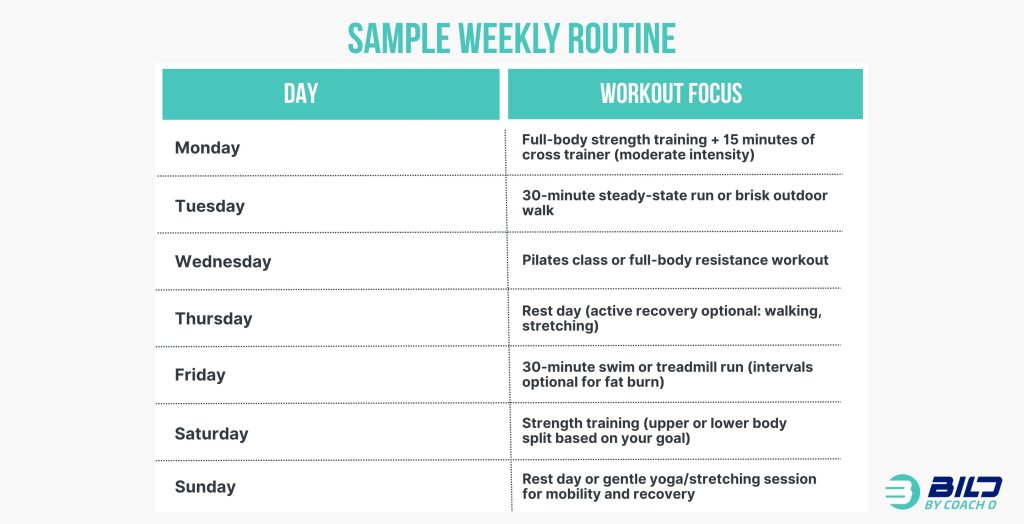
Sample Weekly Routine
Day | Workout Focus |
Monday | Full-body strength training + 15 minutes of cross trainer (moderate intensity) |
Tuesday | 30-minute steady-state run or brisk outdoor walk |
Wednesday | Pilates class or full-body resistance workout |
Thursday | Rest day (active recovery optional: walking, stretching) |
Friday | 30-minute swim or treadmill run (intervals optional for fat burn) |
Saturday | Strength training (upper or lower body split based on your goal) |
Sunday | Rest day or gentle yoga/stretching session for mobility and recovery |
Common Myths About Cardio and Strength Training
Misinformation about fitness slows results and creates confusion. These five myths often block progress and discourage people from starting effective routines.
- Lifting Weights Makes Women Bulky
False. Strength training builds lean muscle, not bulk. Women have lower testosterone levels, which prevents excessive muscle gain. Strength workouts define muscles and enhance body shape. - You Must Do Cardio Every Day to Lose Weight
False. Weight loss depends on a consistent calorie deficit, not daily cardio. Strength and cardio both help burn calories. Three to five total sessions per week is effective for most people. - Cardio Is Better Than Weights for Fat Loss
False. Cardio burns more calories during a workout, but strength training increases fat burn after. Muscle boosts resting metabolism, making strength workouts essential for long-term results. - You Can Target Belly Fat with Crunches
False. Spot reduction is a myth. Fat loss occurs systemically. Compound movements and overall calorie deficit reduce body fat, including belly fat. - Strength Training Is Unsafe for Older Adults
False. Resistance training improves bone density, balance and mobility. It reduces the risk of falls and supports independence well into older age.

Cardio vs Strength Training Based on Fitness Goals
The best results come from matching your workouts to your goals. This breakdown clarifies what each method delivers.
| Fitness Goal | Cardio | Strength Training |
| Fat Loss | Burns calories quickly and creates a calorie deficit | Increases resting metabolism and preserves muscle mass |
| Muscle Building | Supports recovery and cardiovascular health | Stimulates hypertrophy and builds lean muscle |
| Endurance | Improves aerobic capacity, heart function, and lung efficiency | Enhances stability and reduces injury risk during longer sessions |
| Body Recomposition | Accelerates fat reduction for visible changes | Builds lean mass and improves body composition |
| Health & Longevity | Supports heart health, brain function, and circulation | Maintains mobility, bone density, and hormone balance |
Mistakes to Avoid When Doing Cardio and Strength Training
Avoiding these five mistakes helps improve results, reduce injury risk, and maintain long-term progress.
- Skipping recovery days :Your body builds muscle and burns fat during recovery. Training without rest increases fatigue and stalls muscle repair. Aim for 1–2 rest days per week.
- Doing cardio before every strength session: Cardio first depletes energy and reduces lifting performance. If your goal is strength or fat loss, lift before cardio to maintain intensity and muscle output.
- Not using progressive overload: Lifting the same weight or running at the same pace limits progress. Increase resistance, reps, or time every 1–2 weeks to stimulate adaptation.
- Prioritizing speed over form: Fast reps and sloppy technique increase the risk of injury. Focus on control, range of motion, and proper movement to get better results and stay consistent.
- Failing to track workouts: Without tracking, it’s hard to see progress or spot plateaus. Write down the types of exercises, weights, reps, and durations weekly to improve accountability and motivation.

How to Start if You're New to Cardio or Strength Training
Start with simple, consistent workouts to build a strong fitness habit. You don’t need advanced knowledge or equipment to begin. Focus on movements you enjoy and progress gradually.
Set a weekly schedule.
Commit to 3-4 workouts per week, each lasting 20-30 minutes. Choose consistent time blocks that fit your routine.
Pick one method to start
Choose cardio if you enjoy steady movement. Choose strength training if you want to feel stronger fast. Either method supports fat loss.
Learn the basics first.
Use body weight for strength and walking or cycling for cardio. Start with aerobic exercises that match your fitness level.
Focus on form over intensity.
Proper technique prevents injury and improves results. Take time to master the movement before increasing speed or weight.
Track your progress.
Write down your workouts, reps, and how you feel. Tracking builds consistency and highlights improvements over time.
If you need expert guidance, genuine community support or a program built around real-life schedules, BILD by Coach O offers strength and conditioning classes for all levels, including beginners. Best of all, your first class is free.
Join us and see the difference.
